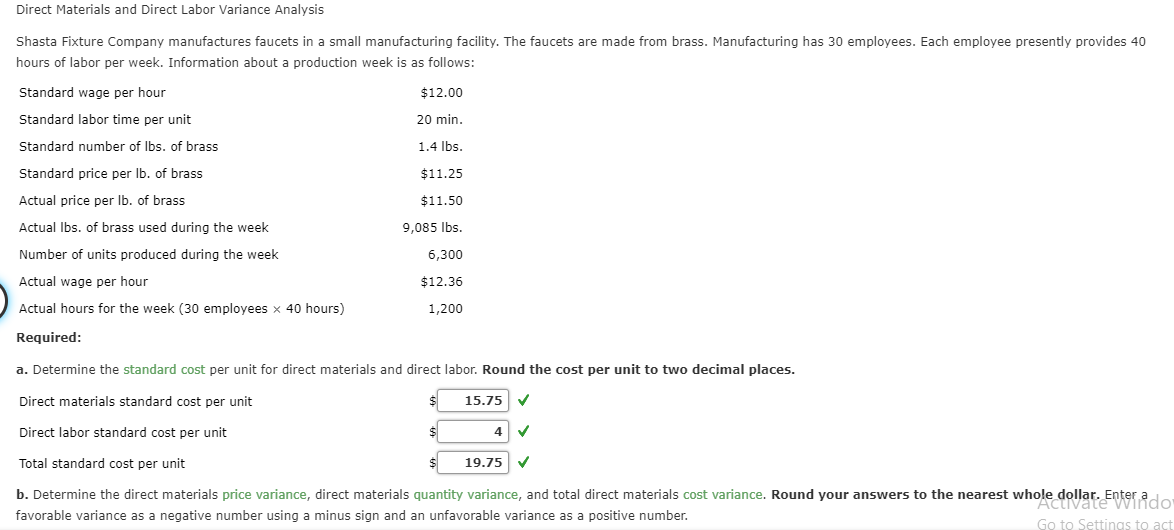
In other words, when actual number of hours worked differ from the standard number of hours allowed to manufacture a certain number of units, labor efficiency variance occurs. They provide valuable insights into the effectiveness of a company’s invoice templates for free labor cost control and workforce utilization. By regularly analyzing labor variances, companies can identify discrepancies between actual and budgeted costs, understand the root causes of these variances, and take corrective actions.
- Kenneth W. Boyd has 30 years of experience in accounting and financial services.
- For example, the variance can be used to evaluate the performance of a company's bargaining staff in setting hourly rates with the company union for the next contract period.
- The actual amounts paid may include extra payments for shift differentials or overtime.
- Direct labor rate variance arise from the difference in actual pay rate of laborers versus what is budgeted.
- Figure 10.7 contains some possible explanations for the laborrate variance (left panel) and labor efficiency variance (rightpanel).
- As a result of this unfavorable outcome information, the company may consider using cheaper labor, changing the production process to be more efficient, or increasing prices to cover labor costs.
How confident are you in your long term financial plan?
The difference in hours is multiplied by the standard price per hour, showing a $1,000 unfavorable direct labor time variance. This is offset by a larger favorable direct labor rate variance of $2,550. The net direct labor cost variance is still $1,550 (favorable), but this additional analysis shows how the time and rate differences contributed to the overall variance. All tasks do not require equally skilled workers; some tasks are more complicated and require more experienced workers than others. This general fact should be kept in mind while assigning tasks to available work force.
Total Direct Labor Variance
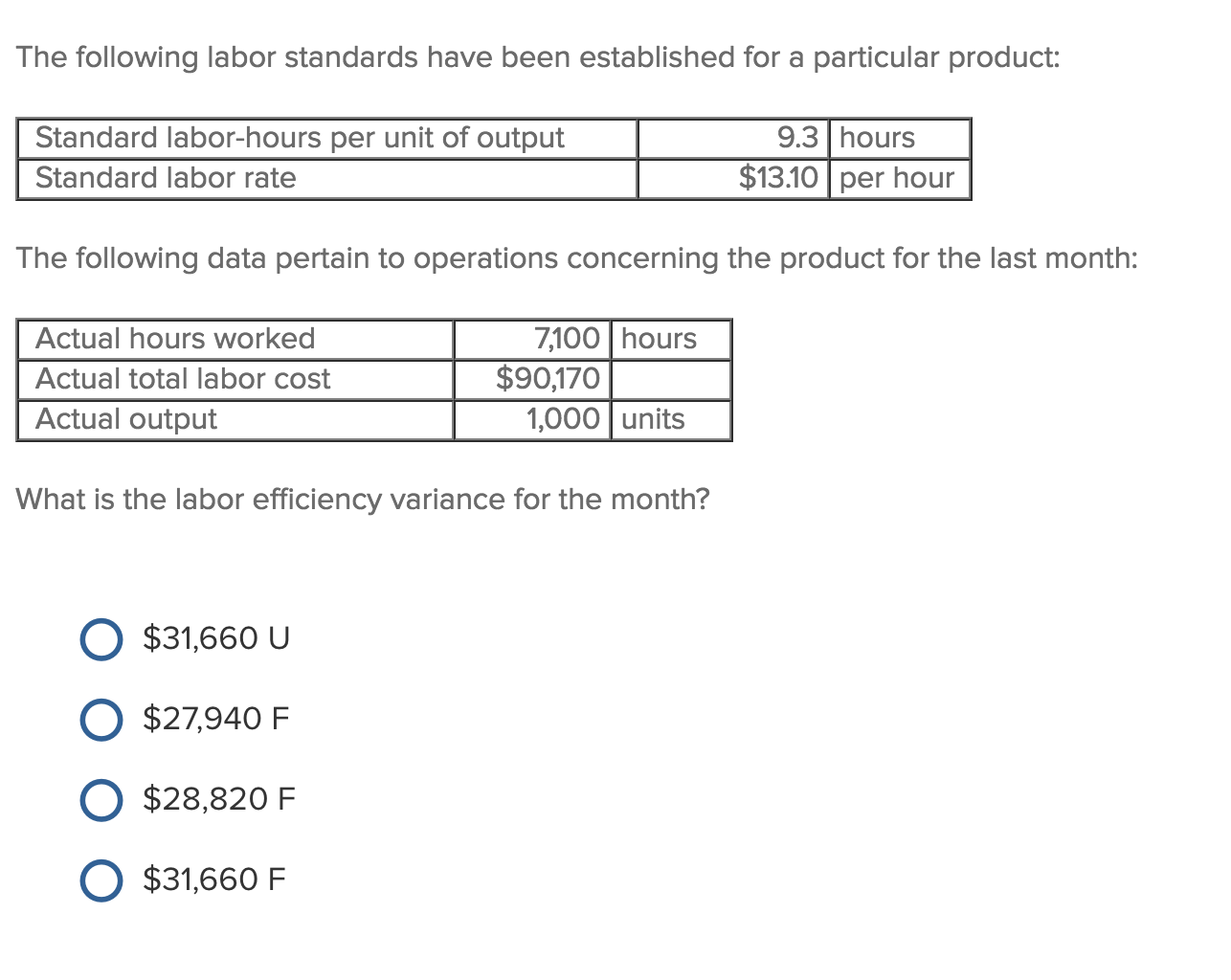
Labor efficiency variance measures the difference between the actual hours worked and the standard hours that should have been worked for the actual production level. It reflects how efficiently labor resources are utilized in the production process. This variance helps businesses understand whether their workforce is working more or fewer hours than expected to produce a given level of output. As with direct materials variances, all positive variances areunfavorable, and all negative variances are favorable. Recall from Figure 10.1 that the standard rate for Jerry’s is$13 per direct labor hour and the standard direct labor hours is0.10 per unit. Figure 10.6 shows how to calculate the labor rateand efficiency variances given the actual results and standardsinformation.
Strategies for Improving Labor Efficiency Variance
Labor mix variance is the difference between the actual mix of labor and standard mix, caused by hiring or training costs. Outcome These corrective actions resulted in a significant reduction in labor efficiency variance. Company B not only improved productivity but also saw a boost in employee morale as workers experienced fewer interruptions and delays in their tasks.
Finance Strategists is a leading financial education organization that connects people with financial professionals, priding itself on providing accurate and reliable financial information to millions of readers each year. This team of experts helps Finance Strategists maintain the highest level of accuracy and professionalism possible. At Finance Strategists, we partner with financial experts to ensure the accuracy of our financial content.
If the tasks that are not so complicated are assigned to very experienced workers, an unfavorable labor rate variance may be the result. The reason is that the highly experienced workers can generally be hired only at expensive wage rates. If, on the other hand, less experienced workers are assigned the complex tasks that require higher level of expertise, a favorable labor rate variance may occur.
However, these workers may cause the quality issues due to lack of expertise and inflate the firm’s internal failure costs. In order to keep the overall direct labor cost inline with standards while maintaining the output quality, it is much important to assign right tasks to right workers. Standard costs are used to establish theflexible budget for direct labor. The flexible budget is comparedto actual costs, and the difference is shown in the form of twovariances. It is defined as the differencebetween the actual number of direct labor hours worked and budgeteddirect labor hours that should have been worked based on thestandards.
Another element this company and others must consider is a direct labor time variance. The human resources manager of Hodgson Industrial Design estimates that the average labor rate for the coming year for Hodgson's production staff will be $25/hour. This estimate is based on a standard mix of personnel at different pay rates, as well as a reasonable proportion of overtime hours worked. Direct labor rate variance arise from the difference in actual pay rate of laborers versus what is budgeted. Since the actual labor rate is lower than the standard rate, the variance is positive and thus favorable. The actual hours used can differ from the standard hours because of improved efficiencies in production, carelessness or inefficiencies in production, or poor estimation when creating the standard usage.
Regular analysis helps in promptly identifying new variances and addressing them before they escalate. Additionally, continuous improvement initiatives, such as enhancing training programs, optimizing workflows, and maintaining favorable working conditions, can lead to sustained productivity gains and cost savings. Understanding both labor rate variance and labor efficiency variance is essential for a comprehensive analysis of direct labor variance.
